EPFL Researchers Develop Injectable Hydrogel to Rapidly Enhance Bone Density
EPFL Researchers Develop Injectable Hydrogel to Rapidly Enhance Bone Density
Scientists at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have developed an innovative injectable hydrogel designed to significantly increase bone density, offering a promising new approach to treating osteoporosis and related bone conditions.
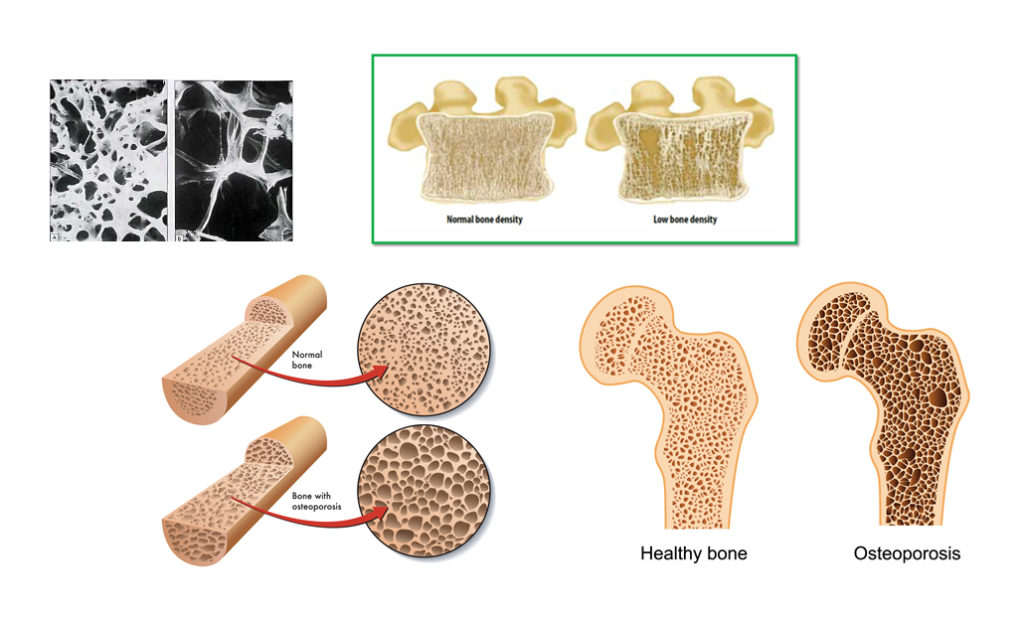
A Novel Composition Mimicking Natural Bone
The hydrogel is composed of hyaluronic acid and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, materials that closely resemble the natural components of bone tissue. This composition allows the hydrogel to integrate seamlessly with existing bone structures, promoting rapid densification at targeted sites.

Significant Results in Preclinical Studies
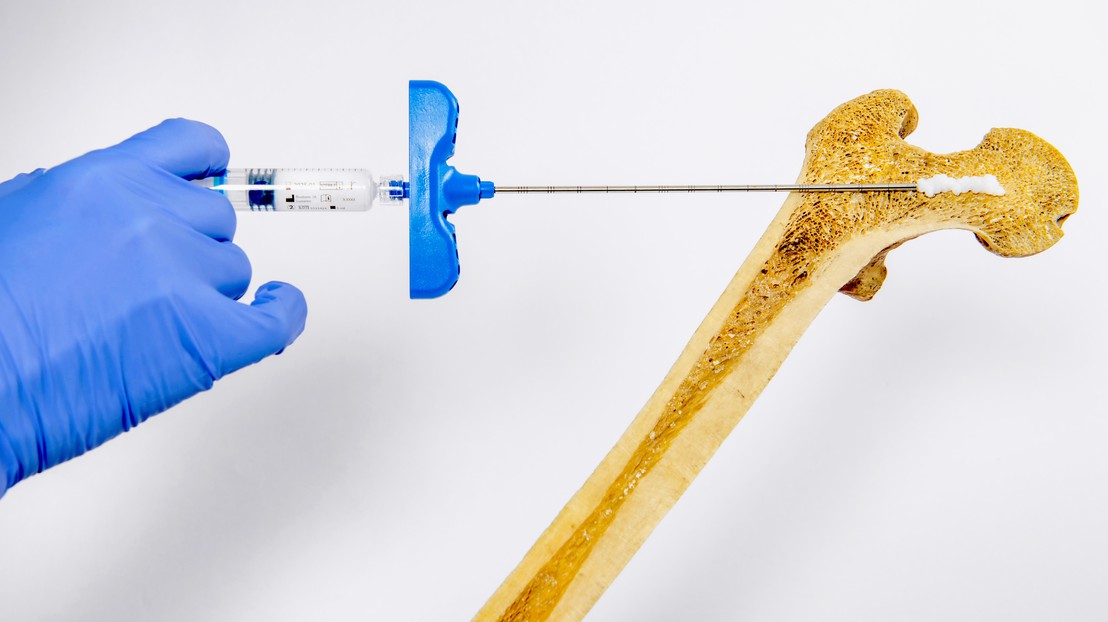
In animal studies, the hydrogel demonstrated remarkable efficacy. When injected into areas of bone loss in rats, it led to a two- to three-fold increase in bone density within just a few weeks. Furthermore, when combined with systemic osteoporosis treatments such as parathyroid hormone and the anti-resorptive drug Zoledronate, the hydrogel achieved up to a 4.8-fold increase in bone density at the injection sites.

Potential for Human Application
The research team, including collaborators from the EPFL spin-off company Flowbone and the Schulthess Klinik in Zurich, is currently seeking regulatory approval to initiate clinical trials in humans. The goal is to validate the hydrogel’s effectiveness in rapidly enhancing bone density, particularly in patients at high risk of fractures or those requiring bone support for implants.
Implications for Osteoporosis Treatment
Traditional osteoporosis treatments often require extended periods to become effective, leaving patients vulnerable to fractures during the interim. The development of this hydrogel presents a potential breakthrough by offering a method to quickly strengthen bone in specific areas, thereby reducing the risk of fractures and improving patient outcomes.